Treating Pressure Injuries: Debridement
The goal of treatment for pressure injuries is to create a healing environment. This may require debridement (removing dead or necrotic tissue) so new cells can form. Various types of debridement are available. These are done by healthcare providers and certified specialists. To control pain during debridement, pain-relieving medicines may be needed.
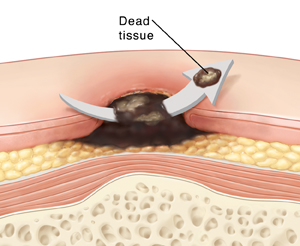 |
| Dead tissue must be removed for the wound to heal properly. Debridement should only be done when there is good blood flow to the wound. |
Sharp debridement removes dead tissue with a scalpel, scissors, or other sharp instrument. Extensive removal may require surgery. Sharp debridement allows for precise removal of tissue and is the preferred method if you have an active infection. This technique can be painful, so it requires adequate pain control medicines. Extensive sharp debridement is done under anesthesia by a surgeon. During this process, the surgeon removes enough dead and damaged tissue until tissue with a good bleeding capillary base is found.
Enzymatic debridement uses topical agents containing enzymes to dissolve dead tissue. They attack the fibrin and collagen of necrotic tissue and exudate. If eschar is present, tiny cuts may need to be made before applying the enzymes to help ensure their absorption. This “cross-hatching” is done by a healthcare provider or specialist.
Autolytic debridement uses the body’s own enzymes to break down necrotic tissue. Special dressings are used to keep the wound moist, allowing the necrotic skin to slowly separate from healthy tissue. Autolytic debridement can take up to several weeks but is less painful than other methods. It’s also selective in the tissue it removes. Autolytic debridement should not be used if you have an active infection.
Biologic debridement is the use of sterile larvae (maggots) that produce powerful enzymes that liquefy and then ingest dead tissue.
Mechanical (irrigation, hydrotherapy, wet-to-moist, wet-to-dry) debridement may be used to remove debris and dead tissue. Wet-to-dry involves applying a piece of gauze moistened with saline to the wound and letting it dry. The dried gauze is then removed, taking tissue and debris with it. This is not a favored method because it may remove healthy tissue as well as dead tissue. Wet-to-dry debridement can also be quite painful.